Hybrid Recommendation System for Yelp Data
Introduction
In the modern digital landscape, recommendation systems play a pivotal role in personalizing user experiences. From suggesting movies on Netflix to recommending restaurants on Yelp, these systems help users discover content that aligns with their preferences while boosting platform engagement.
This blog delves into the development of a hybrid recommendation system built for a Yelp dataset as part of a data mining competition at USC. The hybrid system combines the strengths of two powerful approaches:
- Item-Based Collaborative Filtering
- Model-Based Collaborative Filtering
The final model achieves impressive performance, with a Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) of 0.97, showcasing its effectiveness in predicting user ratings accurately.
Problem Statement
The goal was to predict user ratings for businesses based on historical Yelp data. The primary challenge lay in designing a system capable of generalizing across diverse user and business attributes while addressing the inherent sparsity of the dataset.
The Yelp Dataset
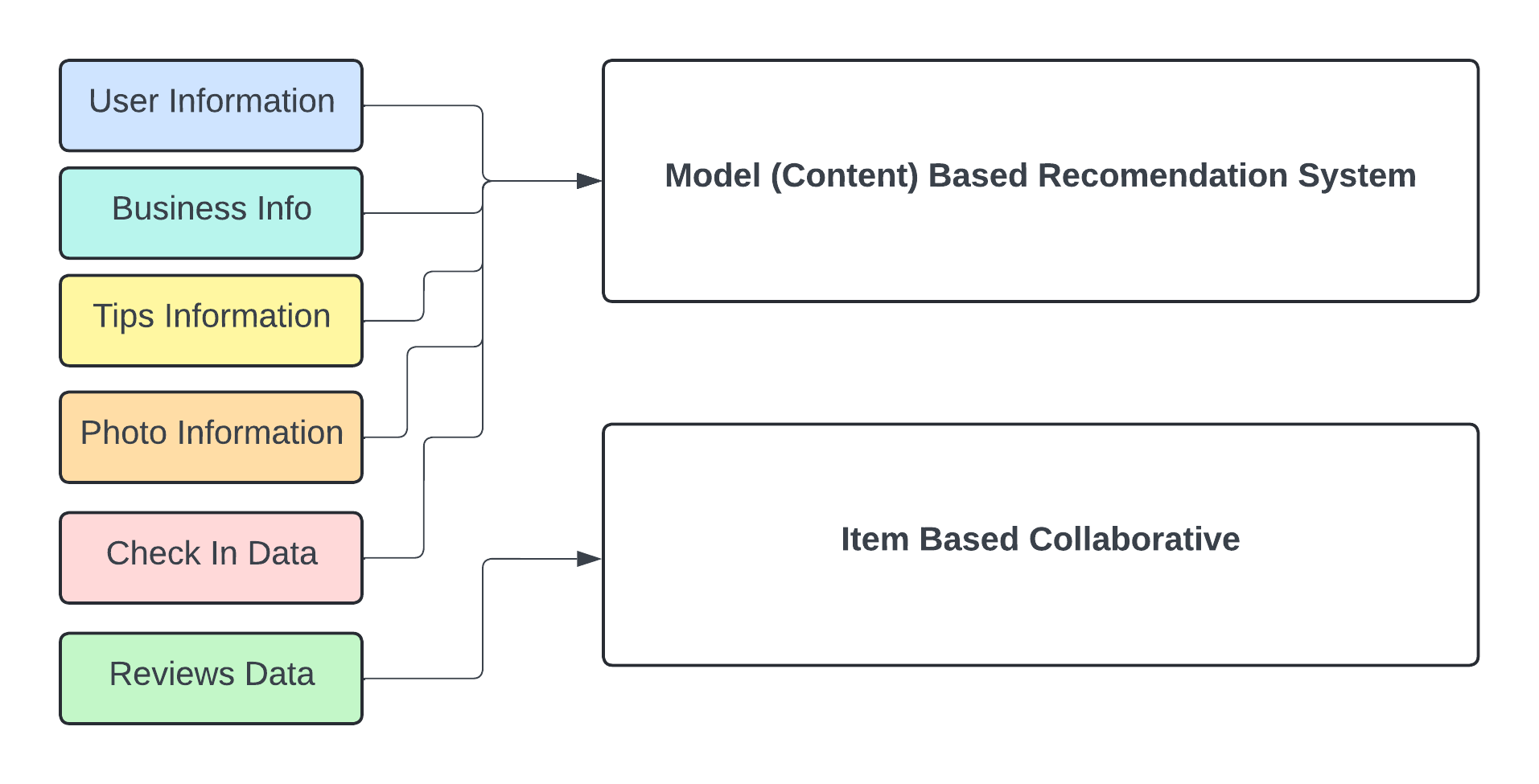
The recommendation system leveraged the Yelp Dataset, a rich collection of data spanning various domains such as businesses, user reviews, tips, photos, and check-ins. Specifically, the dataset comprises several key files:
-
User Data (
user.json): Contains user-level information such as review counts, average star ratings given by the users, and compliments received across multiple categories (e.g., funny, cool, useful). -
Business Data (
business.json): Details attributes of businesses including their location, categories, average star ratings, review counts, and operational status (open or closed). -
Reviews (
review_train.json): User reviews that include ratings, textual feedback, and associated user and business identifiers. -
Tips (
tip.json): Short textual tips left by users for businesses, including the number of likes each tip received. -
Photos (
photo.json): Photos associated with businesses, categorized by labels (e.g., food, interior, exterior). -
Check-ins (
checkin.json): Check-in data indicating user engagement, including average daily check-ins and total check-in counts.
These files collectively provided comprehensive insights for robust feature engineering and accurate modeling.
Methodology
Overview
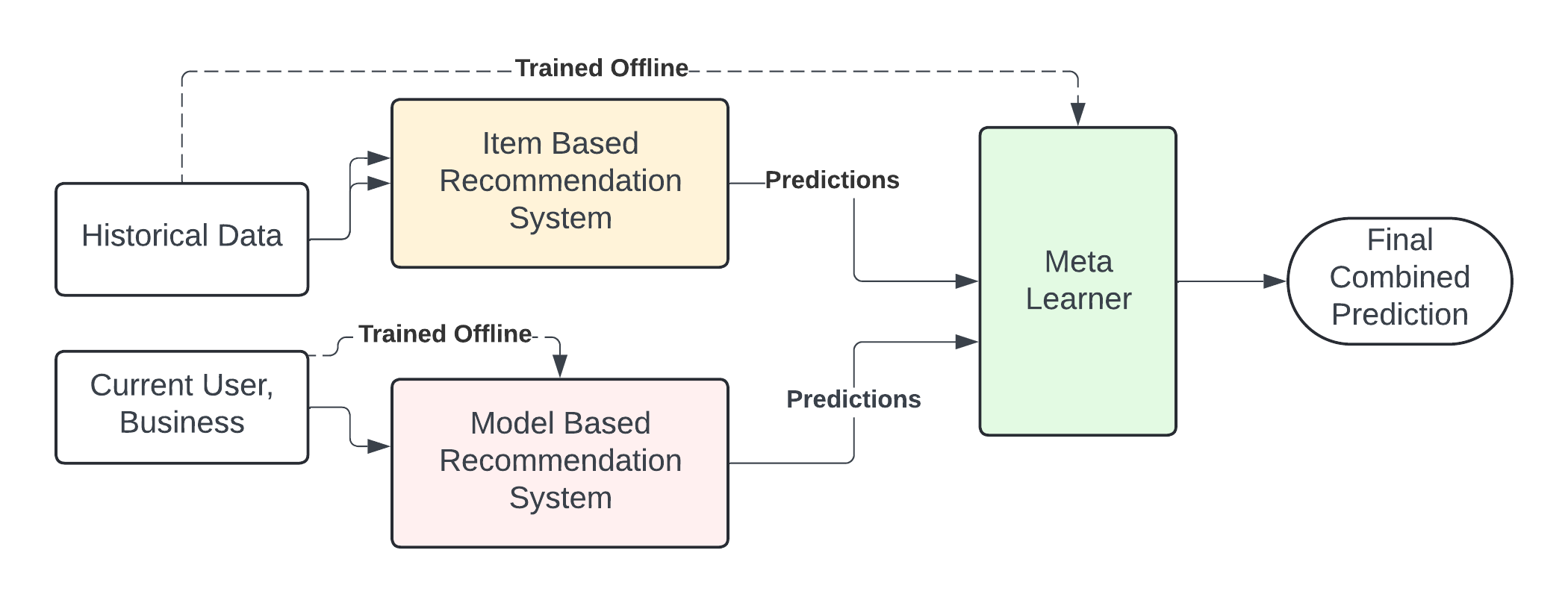
To tackle the problem, a hybrid recommendation system was developed that leverages predictions from:
- Item-Based Collaborative Filtering, which computes similarities between items based on user ratings.
- Model-Based Collaborative Filtering, which employs machine learning techniques to model complex interactions between users and businesses.
A third layer, the meta-learner, combines predictions from the two systems to enhance accuracy further.
Item-Based Collaborative Filtering
This approach predicts ratings by analyzing the similarity between items based on user ratings. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Steps:
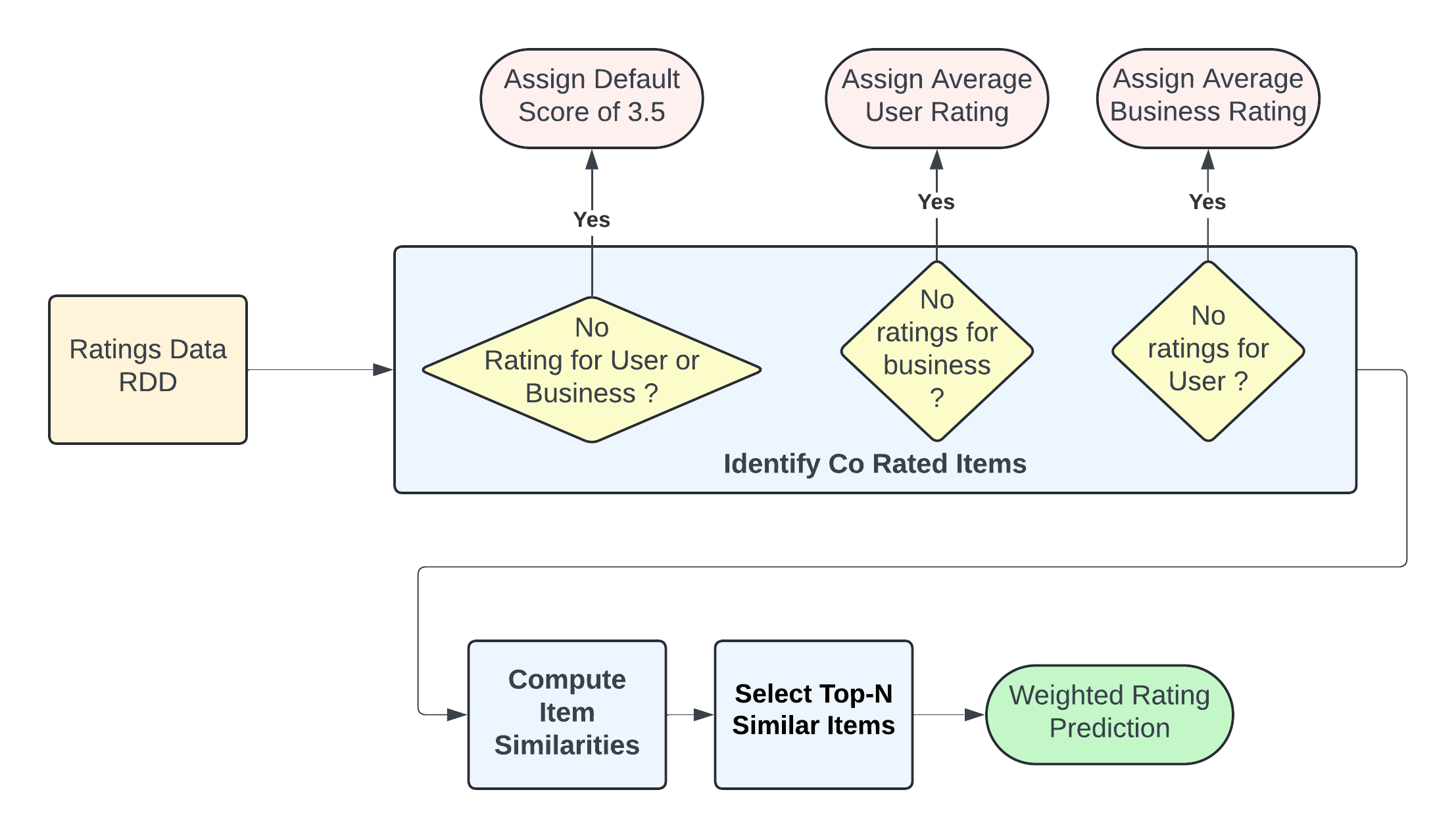
- Data Representation:
- User-business interaction data was loaded into a distributed environment using Apache Spark and represented as a sparse matrix (RDD).
- Default Voting Mechanism:
- For user-business pairs with no interaction data, a default rating of 3.5 (neutral rating) was assigned.
- If only one type of data (user or business) was available, the average rating of the available data was used.
- Co-Rated Item Identification:
- Users who rated both items were identified via distributed joins on the RDDs of user-business ratings.
- Pearson Correlation Calculation:
- The Pearson correlation formula computed item similarities, leveraging distributed computations in Spark.
- Top-N Similar Items:
- The top 14 most similar items for the target item were selected.
- Weighted Rating Prediction:
- Ratings were predicted as a weighted sum of neighbor ratings.
Model-Based Collaborative Filtering
This component utilizes machine learning to predict ratings based on user and business attributes.
Feature Engineering and Processing:
- User Features: Review count, average stars, compliments.
- Business Features: Stars, review counts, operational status, tips, likes.
- Supplementary Features: One-hot encoded photo attributes, check-in statistics.
Model Training and Hyperparameter Tuning:
- An XGBoost Regressor was trained with Spark-generated features.
- Hyperparameters were optimized through extensive grid search.

Meta-Learner
The meta-learner combined predictions from both collaborative filtering methods using an XGBoost Regressor.
Evaluation Metrics
To rigorously evaluate the system’s performance, several metrics were employed:
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): Primary evaluation metric; achieved RMSE: 0.977.
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE): Evaluated average prediction errors.
- Error Distribution: Categorized errors to analyze prediction accuracy.
- Missed Predictions: Managed with default voting mechanisms.
---------------- Evaluation Metrics ----------------
Misses (No predictions found): 0
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 0.7599779602241632
Following differences are calculated as p - a where p is predicted and a is actual
Distribution of Absolute Differences:
>=0 and <1: n = 102613
>=1 and <2: n = 32589
>=2 and <3: n = 6049
>=3 and <4: n = 793
>=4: n = 0
Distribution of Differences (p - a):
>=-1 and <0: n = 61401
>=0 and <1: n = 41212
>=-2 and <-1: n = 17311
>=1 and <2: n = 15278
>=2 and <3: n = 5218
>=-3 and <-2: n = 831
>=3 and <4: n = 781
>=-4 and <-3: n = 12
>=4: n = 0
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): 0.9739361309397205
Conclusion
The hybrid recommendation system effectively combined collaborative filtering techniques and advanced machine learning methodologies, delivering highly accurate predictions for Yelp data. Leveraging the extensive Yelp dataset and Apache Spark’s capabilities significantly enhanced the system’s performance.
GitHub Repository and Code
The complete codebase for the recommendation system is available on GitHub: yelp-recommendation-system
Future Directions
- Incorporate contextual real-time data.
- Explore deep learning methodologies.
- Optimize for real-time deployment.
References
- Scikit-Learn Documentation
- XGBoost Documentation
- Apache Spark Documentation